Tornado
| Tornado | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Area of occurrence | North America (particularly in central and southeastern regions of the United States colloquially known as Tornado Alley), South Africa, much of Europe (except most of the Alps), western and eastern Australia, New Zealand, Bangladesh and adjacent eastern India, Japan, the Philippines, and southeastern South America (Uruguay and Argentina) |
| Season | Primarily spring and summer, but can occur at any time of year with the right atmospheric conditions |
| Effect | Wind damage |
| Part of a series on |
| Weather |
|---|
|
|
A tornado is a violently rotating column of air that is in contact with both the surface of the Earth and a cumulonimbus cloud or, in rare cases, the base of a cumulus cloud. It is often referred to as a twister, whirlwind or cyclone,[1] although the word cyclone is used in meteorology to name a weather system with a low-pressure area in the center around which, from an observer looking down toward the surface of the Earth, winds blow counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern.[2] Tornadoes come in many shapes and sizes, and they are often (but not always) visible in the form of a condensation funnel originating from the base of a cumulonimbus cloud, with a cloud of rotating debris and dust beneath it. Most tornadoes have wind speeds less than 180 kilometers per hour (110 miles per hour), are about 80 meters (250 feet) across, and travel several kilometers (a few miles) before dissipating. The most extreme tornadoes can attain wind speeds of more than 480 kilometers per hour (300 mph), can be more than 3 kilometers (2 mi) in diameter, and can stay on the ground for more than 100 km (62 mi).[3][4][5]
Various types of tornadoes include the multiple-vortex tornado, landspout, and waterspout. Waterspouts are characterized by a spiraling funnel-shaped wind current, connecting to a large cumulus or cumulonimbus cloud. They are generally classified as non-supercellular tornadoes that develop over bodies of water, but there is disagreement over whether to classify them as true tornadoes. These spiraling columns of air frequently develop in tropical areas close to the equator and are less common at high latitudes.[6] Other tornado-like phenomena that exist in nature include the gustnado, dust devil, fire whirl, and steam devil.
Tornadoes occur most frequently in North America (particularly in central and southeastern regions of the United States colloquially known as Tornado Alley; the United States has by far the most tornadoes of any country in the world).[7] Tornadoes also occur in South Africa, much of Europe (except most of the Alps), western and eastern Australia, New Zealand, Bangladesh and adjacent eastern India, Japan, the Philippines, and southeastern South America (Uruguay and Argentina).[8][9] Tornadoes can be detected before or as they occur through the use of pulse-Doppler radar by recognizing patterns in velocity and reflectivity data, such as hook echoes or debris balls, as well as through the efforts of storm spotters.[10][11]
Tornado rating scales
There are several scales for rating the strength of tornadoes. The Fujita scale rates tornadoes by damage caused and has been replaced in some countries by the updated Enhanced Fujita Scale. An F0 or EF0 tornado, the weakest category, damages trees, but not substantial structures. An F5 or EF5 tornado, the strongest category, rips buildings off their foundations and can deform large skyscrapers. The similar TORRO scale ranges from T0 for extremely weak tornadoes to T11 for the most powerful known tornadoes.[12] The International Fujita scale is also used to rate the intensity of tornadoes and other wind events based on the severity of the damage they cause.[13] Doppler radar data, photogrammetry, and ground swirl patterns (trochoidal marks) may also be analyzed to determine intensity and assign a rating.[14][15]


Etymology
The word tornado comes from the Spanish tronada (meaning 'thunderstorm', past participle of tronar 'to thunder', itself in turn from the Latin tonāre 'to thunder').[16][17] The metathesis of the r and o in the English spelling was influenced by the Spanish tornado (past participle of tornar 'to twist, turn,', from Latin tornō 'to turn').[16] The English word has been reborrowed into Spanish, referring to the same weather phenomenon.
Tornadoes' opposite phenomena are the widespread, straight-line derechos (/dəˈreɪtʃoʊ/, from Spanish: derecho Spanish pronunciation: [deˈɾetʃo], 'straight'). A tornado is also commonly referred to as a "twister" or the old-fashioned colloquial term cyclone.[18][19]
Definitions
A tornado is a violently rotating column of air, in contact with the ground, either pendant from a cumuliform cloud or underneath a cumuliform cloud, and often (but not always) visible as a funnel cloud.[20] For a vortex to be classified as a tornado, it must be in contact with both the ground and the cloud base. The term is not precisely defined; for example, there is disagreement as to whether separate touchdowns of the same funnel constitute separate tornadoes.[5] Tornado refers to the vortex of wind, not the condensation cloud.[21][22]
Funnel cloud

A tornado is not necessarily visible; however, the intense low pressure caused by the high wind speeds (as described by Bernoulli's principle) and rapid rotation (due to cyclostrophic balance) usually cause water vapor in the air to condense into cloud droplets due to adiabatic cooling. This results in the formation of a visible funnel cloud or condensation funnel.[23]
There is some disagreement over the definition of a funnel cloud and a condensation funnel. According to the Glossary of Meteorology, a funnel cloud is any rotating cloud pendant from a cumulus or cumulonimbus, and thus most tornadoes are included under this definition.[24] Among many meteorologists, the "funnel cloud" term is strictly defined as a rotating cloud which is not associated with strong winds at the surface, and condensation funnel is a broad term for any rotating cloud below a cumuliform cloud.[5]
Tornadoes often begin as funnel clouds with no associated strong winds at the surface, and not all funnel clouds evolve into tornadoes. Most tornadoes produce strong winds at the surface while the visible funnel is still above the ground, so it is difficult to discern the difference between a funnel cloud and a tornado from a distance.[5]
Outbreaks and families
Occasionally, a single storm will produce more than one tornado, either simultaneously or in succession. Multiple tornadoes produced by the same storm cell are referred to as a "tornado family".[25] Several tornadoes are sometimes spawned from the same large-scale storm system. If there is no break in activity, this is considered a tornado outbreak (although the term "tornado outbreak" has various definitions). A period of several successive days with tornado outbreaks in the same general area (spawned by multiple weather systems) is a tornado outbreak sequence, occasionally called an extended tornado outbreak.[20][26][27]
Characteristics
Size and shape
Most tornadoes take on the appearance of a narrow funnel, a few hundred meters (yards) across, with a small cloud of debris near the ground. Tornadoes may be obscured completely by rain or dust. These tornadoes are especially dangerous, as even experienced meteorologists might not see them.[28]
Small, relatively weak landspouts may be visible only as a small swirl of dust on the ground. Although the condensation funnel may not extend all the way to the ground, if associated surface winds are greater than 64 km/h (40 mph), the circulation is considered a tornado.[21] A tornado with a nearly cylindrical profile and relatively low height is sometimes referred to as a "stovepipe" tornado. Large tornadoes which appear at least as wide as their cloud-to-ground height can look like large wedges stuck into the ground, and so are known as "wedge tornadoes" or "wedges".[29] The "stovepipe" classification is also used for this type of tornado if it otherwise fits that profile. A wedge can be so wide that it appears to be a block of dark clouds, wider than the distance from the cloud base to the ground. Even experienced storm observers may not be able to tell the difference between a low-hanging cloud and a wedge tornado from a distance. Many, but not all major tornadoes are wedges.[29]
Tornadoes in the dissipating stage can resemble narrow tubes or ropes, and often curl or twist into complex shapes. These tornadoes are said to be "roping out", or becoming a "rope tornado". When they rope out, the length of their funnel increases, which forces the winds within the funnel to weaken due to conservation of angular momentum.[30] Multiple-vortex tornadoes can appear as a family of swirls circling a common center, or they may be completely obscured by condensation, dust, and debris, appearing to be a single funnel.[31]
In the United States, tornadoes are around 500 feet (150 m) across on average.[28] However, there is a wide range of tornado sizes. Weak tornadoes, or strong yet dissipating tornadoes, can be exceedingly narrow, sometimes only a few feet or couple meters across. One tornado was reported to have a damage path only 7 feet (2.1 m) long.[28] On the other end of the spectrum, wedge tornadoes can have a damage path a mile (1.6 km) wide or more. A tornado that affected Hallam, Nebraska on May 22, 2004, was up to 2.5 miles (4.0 km) wide at the ground, and a tornado in El Reno, Oklahoma on May 31, 2013, was approximately 2.6 miles (4.2 km) wide, the widest on record.[4][32]
Track length
In the United States, the average tornado travels on the ground for 5 miles (8.0 km). However, tornadoes are capable of both much shorter and much longer damage paths: one tornado was reported to have a damage path only 7 feet (2.1 m) long, while the record-holding tornado for path length—the Tri-State Tornado, which affected parts of Missouri, Illinois, and Indiana on March 18, 1925—was on the ground continuously for 219 miles (352 km).[28] Many tornadoes which appear to have path lengths of 100 miles (160 km) or longer are composed of a family of tornadoes which have formed in quick succession; however, there is no substantial evidence that this occurred in the case of the Tri-State Tornado.[26] In fact, modern reanalysis of the path suggests that the tornado may have begun 15 miles (24 km) further west than previously thought.[33]
Appearance

Tornadoes can have a wide range of colors, depending on the environment in which they form. Those that form in dry environments can be nearly invisible, marked only by swirling debris at the base of the funnel. Condensation funnels that pick up little or no debris can be gray to white. While traveling over a body of water (as a waterspout), tornadoes can turn white or even blue. Slow-moving funnels, which ingest a considerable amount of debris and dirt, are usually darker, taking on the color of debris. Tornadoes in the Great Plains can turn red because of the reddish tint of the soil, and tornadoes in mountainous areas can travel over snow-covered ground, turning white.[28]
Lighting conditions are a major factor in the appearance of a tornado. A tornado which is "back-lit" (viewed with the sun behind it) appears very dark. The same tornado, viewed with the sun at the observer's back, may appear gray or brilliant white. Tornadoes which occur near the time of sunset can be many different colors, appearing in hues of yellow, orange, and pink.[18][35]
Dust kicked up by the winds of the parent thunderstorm, heavy rain and hail, and the darkness of night are all factors that can reduce the visibility of tornadoes. Tornadoes occurring in these conditions are especially dangerous, since only weather radar observations, or possibly the sound of an approaching tornado, serve as any warning to those in the storm's path. Most significant tornadoes form under the storm's updraft base, which is rain-free,[36] making them visible.[37] Also, most tornadoes occur in the late afternoon, when the bright sun can penetrate even the thickest clouds.[26]
There is mounting evidence, including Doppler on Wheels mobile radar images and eyewitness accounts, that most tornadoes have a clear, calm center with extremely low pressure, akin to the eye of tropical cyclones. Lightning is said to be the source of illumination for those who claim to have seen the interior of a tornado.[38][39][40]
Rotation
Tornadoes normally rotate cyclonically (when viewed from above, this is counterclockwise in the northern hemisphere and clockwise in the southern). While large-scale storms always rotate cyclonically due to the Coriolis effect, thunderstorms and tornadoes are so small that the direct influence of the Coriolis effect is negligible, as indicated by their large Rossby numbers. Supercells and tornadoes rotate cyclonically in numerical simulations even when the Coriolis effect is neglected.[41][42] Low-level mesocyclones and tornadoes owe their rotation to complex processes within the supercell and ambient environment.[43]
Approximately 1 percent of tornadoes rotate in an anticyclonic direction in the northern hemisphere. Typically, systems as weak as landspouts and gustnadoes can rotate anticyclonically, and usually only those which form on the anticyclonic shear side of the descending rear flank downdraft (RFD) in a cyclonic supercell.[44] On rare occasions, anticyclonic tornadoes form in association with the mesoanticyclone of an anticyclonic supercell, in the same manner as the typical cyclonic tornado, or as a companion tornado either as a satellite tornado or associated with anticyclonic eddies within a supercell.[45]
Sound and seismology

Tornadoes emit widely on the acoustics spectrum and the sounds are caused by multiple mechanisms. Various sounds of tornadoes have been reported, mostly related to familiar sounds for the witness and generally some variation of a whooshing roar. Popularly reported sounds include a freight train, rushing rapids or waterfall, a nearby jet engine, or combinations of these. Many tornadoes are not audible from much distance; the nature of and the propagation distance of the audible sound depends on atmospheric conditions and topography.[5]
The winds of the tornado vortex and of constituent turbulent eddies, as well as airflow interaction with the surface and debris, contribute to the sounds. Funnel clouds also produce sounds. Funnel clouds and small tornadoes are reported as whistling, whining, humming, or the buzzing of innumerable bees or electricity, or more or less harmonic, whereas many tornadoes are reported as a continuous, deep rumbling, or an irregular sound of "noise".[46]
Since many tornadoes are audible only when very near, sound is not to be thought of as a reliable warning signal for a tornado. Tornadoes are also not the only source of such sounds in severe thunderstorms; any strong, damaging wind, a severe hail volley, or continuous thunder in a thunderstorm may produce a roaring sound.[47]
Tornadoes also produce identifiable inaudible infrasonic signatures.[48]
Unlike audible signatures, tornadic signatures have been isolated; due to the long-distance propagation of low-frequency sound, efforts are ongoing to develop tornado prediction and detection devices with additional value in understanding tornado morphology, dynamics, and creation.[49] Tornadoes also produce a detectable seismic signature, and research continues on isolating it and understanding the process.[50]
Electromagnetic, lightning, and other effects
Tornadoes emit on the electromagnetic spectrum, with sferics and E-field effects detected.[49][51][52] There are observed correlations between tornadoes and patterns of lightning. Tornadic storms do not contain more lightning than other storms and some tornadic cells never produce lightning at all. More often than not, overall cloud-to-ground (CG) lightning activity decreases as a tornado touches the surface and returns to the baseline level when the tornado dissipates. In many cases, intense tornadoes and thunderstorms exhibit an increased and anomalous dominance of positive polarity CG discharges.[53]
Luminosity has been reported in the past and is probably due to misidentification of external light sources such as lightning, city lights, and power flashes from broken lines, as internal sources are now uncommonly reported and are not known to ever have been recorded. In addition to winds, tornadoes also exhibit changes in atmospheric variables such as temperature, moisture, and atmospheric pressure. For example, on June 24, 2003, near Manchester, South Dakota, a probe measured a 100-millibar (100 hPa; 3.0 inHg) pressure decrease. The pressure dropped gradually as the vortex approached then dropped extremely rapidly to 850 mbar (850 hPa; 25 inHg) in the core of the violent tornado before rising rapidly as the vortex moved away, resulting in a V-shape pressure trace. Temperature tends to decrease and moisture content to increase in the immediate vicinity of a tornado.[54]
Life cycle
Supercell relationship
Tornadoes often develop from a class of thunderstorms known as supercells. Supercells contain mesocyclones, an area of organized rotation a few kilometers/miles up in the atmosphere, usually 1.6–9.7 km (1–6 miles) across. Most intense tornadoes (EF3 to EF5 on the Enhanced Fujita Scale) develop from supercells. In addition to tornadoes, very heavy rain, frequent lightning, strong wind gusts, and hail are common in such storms.[55][56]
Most tornadoes from supercells follow a recognizable life cycle which begins when increasing rainfall drags with it an area of quickly descending air known as the rear flank downdraft (RFD). This downdraft accelerates as it approaches the ground, and drags the supercell's rotating mesocyclone towards the ground with it.[21]
Formation

As the mesocyclone lowers below the cloud base, it begins to take in cool, moist air from the downdraft region of the storm. The convergence of warm air in the updraft and cool air causes a rotating wall cloud to form. The RFD also focuses the mesocyclone's base, causing it to draw air from a smaller and smaller area on the ground. As the updraft intensifies, it creates an area of low pressure at the surface. This pulls the focused mesocyclone down, in the form of a visible condensation funnel. As the funnel descends, the RFD also reaches the ground, fanning outward and creating a gust front that can cause severe damage a considerable distance from the tornado. Usually, the funnel cloud begins causing damage on the ground (becoming a tornado) within a few minutes of the RFD reaching the ground.[21][57] Many other aspects of tornado formation (such as why some storms form tornadoes while others do not, or what precise role downdrafts, temperature, and moisture play in tornado formation) are still poorly understood.[58]
Maturity

Initially, the tornado has a good source of warm, moist air flowing inward to power it, and it grows until it reaches the "mature stage". This can last from a few minutes to more than an hour, and during that time a tornado often causes the most damage, and in rare cases can be more than 1.6 km (1 mile) across. The low pressured atmosphere at the base of the tornado is essential to the endurance of the system.[59] Meanwhile, the RFD, now an area of cool surface winds, begins to wrap around the tornado, cutting off the inflow of warm air which previously fed the tornado.[21] The flow inside the funnel of the tornado is downward, supplying water vapor from the cloud above. This is contrary to the upward flow inside hurricanes, supplying water vapor from the warm ocean below. Therefore, the energy of the tornado is supplied from the cloud above. [60][61]
Dissipation

As the RFD completely wraps around and chokes off the tornado's air supply, the vortex begins to weaken, becoming thin and rope-like. This is the "dissipating stage", often lasting no more than a few minutes, after which the tornado ends. During this stage, the shape of the tornado becomes highly influenced by the winds of the parent storm, and can be blown into fantastic patterns.[26][34][35] Even though the tornado is dissipating, it is still capable of causing damage. The storm is contracting into a rope-like tube and, due to conservation of angular momentum, winds can increase at this point.[30]
As the tornado enters the dissipating stage, its associated mesocyclone often weakens as well, as the rear flank downdraft cuts off the inflow powering it. Sometimes, in intense supercells, tornadoes can develop cyclically. As the first mesocyclone and associated tornado dissipate, the storm's inflow may be concentrated into a new area closer to the center of the storm and possibly feed a new mesocyclone. If a new mesocyclone develops, the cycle may start again, producing one or more new tornadoes. Occasionally, the old (occluded) mesocyclone and the new mesocyclone produce a tornado at the same time.[citation needed]
Although this is a widely accepted theory for how most tornadoes form, live, and die, it does not explain the formation of smaller tornadoes, such as landspouts, long-lived tornadoes, or tornadoes with multiple vortices. These each have different mechanisms which influence their development—however, most tornadoes follow a pattern similar to this one.[62]
Types
Multiple vortex
A multiple-vortex tornado is a type of tornado in which two or more columns of spinning air rotate about their own axes and at the same time revolve around a common center. A multi-vortex structure can occur in almost any circulation, but is very often observed in intense tornadoes. These vortices often create small areas of heavier damage along the main tornado path.[5][21] This is a phenomenon that is distinct from a satellite tornado, which is a smaller tornado that forms very near a large, strong tornado contained within the same mesocyclone. The satellite tornado may appear to "orbit" the larger tornado (hence the name), giving the appearance of one, large multi-vortex tornado. However, a satellite tornado is a distinct circulation, and is much smaller than the main funnel.[5]
Waterspout

A waterspout is defined by the National Weather Service as a tornado over water. However, researchers typically distinguish "fair weather" waterspouts from tornadic (i.e. associated with a mesocyclone) waterspouts. Fair weather waterspouts are less severe but far more common, and are similar to dust devils and landspouts. They form at the bases of cumulus congestus clouds over tropical and subtropical waters. They have relatively weak winds, smooth laminar walls, and typically travel very slowly. They occur most commonly in the Florida Keys and in the northern Adriatic Sea.[63][64][65] In contrast, tornadic waterspouts are stronger tornadoes over water. They form over water similarly to mesocyclonic tornadoes, or are stronger tornadoes which cross over water. Since they form from severe thunderstorms and can be far more intense, faster, and longer-lived than fair weather waterspouts, they are more dangerous.[66] In official tornado statistics, waterspouts are generally not counted unless they affect land, though some European weather agencies count waterspouts and tornadoes together.[5][67]
Landspout
A landspout, or dust-tube tornado, is a tornado not associated with a mesocyclone. The name stems from their characterization as a "fair weather waterspout on land". Waterspouts and landspouts share many defining characteristics, including relative weakness, short lifespan, and a small, smooth condensation funnel that often does not reach the surface. Landspouts also create a distinctively laminar cloud of dust when they make contact with the ground, due to their differing mechanics from true mesoform tornadoes. Though usually weaker than classic tornadoes, they can produce strong winds which could cause serious damage.[5][21]
Similar circulations
Gustnado
A gustnado, or gust front tornado, is a small, vertical swirl associated with a gust front or downburst. Because they are not connected with a cloud base, there is some debate as to whether or not gustnadoes are tornadoes. They are formed when fast-moving cold, dry outflow air from a thunderstorm is blown through a mass of stationary, warm, moist air near the outflow boundary, resulting in a "rolling" effect (often exemplified through a roll cloud). If low level wind shear is strong enough, the rotation can be turned vertically or diagonally and make contact with the ground. The result is a gustnado.[5][68] They usually cause small areas of heavier rotational wind damage among areas of straight-line wind damage.[citation needed]
Dust devil

A dust devil (also known as a whirlwind) resembles a tornado in that it is a vertical swirling column of air. However, they form under clear skies and are no stronger than the weakest tornadoes. They form when a strong convective updraft is formed near the ground on a hot day. If there is enough low-level wind shear, the column of hot, rising air can develop a small cyclonic motion that can be seen near the ground. They are not considered tornadoes because they form during fair weather and are not associated with any clouds. However, they can, on occasion, result in major damage.[28][69]
Fire whirls
Small-scale, tornado-like circulations can occur near any intense surface heat source. Those that occur near intense wildfires are called fire whirls. They are not considered tornadoes, except in the rare case where they connect to a pyrocumulus or other cumuliform cloud above. Fire whirls usually are not as strong as tornadoes associated with thunderstorms. They can, however, produce significant damage.[26]
Steam devils
A steam devil is a rotating updraft between 50-and-200-metre wide (160 and 660 ft) that involves steam or smoke. These formations do not involve high wind speeds, only completing a few rotations per minute. Steam devils are very rare. They most often form from smoke issuing from a power plant's smokestack. Hot springs and deserts may also be suitable locations for a tighter, faster-rotating steam devil to form. The phenomenon can occur over water, when cold arctic air passes over relatively warm water.[28]
Intensity and damage
| F0 EF0 |
F1 EF1 |
F2 EF2 |
F3 EF3 |
F4 EF4 |
F5 EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weak | Strong | Violent | |||
| Significant | |||||
| Intense | |||||
The Fujita scale, Enhanced Fujita scale (EF), and International Fujita scale rate tornadoes by damage caused. The EF scale was an update to the older Fujita scale, by expert elicitation, using engineered wind estimates and better damage descriptions. The EF scale was designed so that a tornado rated on the Fujita scale would receive the same numerical rating, and was implemented starting in the United States in 2007. An EF0 tornado will probably damage trees but not substantial structures, whereas an EF5 tornado can rip buildings off their foundations leaving them bare and even deform large skyscrapers. The similar TORRO scale ranges from a T0 for extremely weak tornadoes to T11 for the most powerful known tornadoes. Doppler weather radar data, photogrammetry, and ground swirl patterns (cycloidal marks) may also be analyzed to determine intensity and award a rating.[5][71][72]

Tornadoes vary in intensity regardless of shape, size, and location, though strong tornadoes are typically larger than weak tornadoes. The association with track length and duration also varies, although longer track tornadoes tend to be stronger.[73] In the case of violent tornadoes, only a small portion of the path is of violent intensity, most of the higher intensity from subvortices.[26]
In the United States, 80% of tornadoes are EF0 and EF1 (T0 through T3) tornadoes. The rate of occurrence drops off quickly with increasing strength—less than 1% are violent tornadoes (EF4, T8 or stronger).[74] Current records may significantly underestimate the frequency of strong (EF2-EF3) and violent (EF4-EF5) tornadoes, as damage-based intensity estimates are limited to structures and vegetation that a tornado impacts. A tornado may be much stronger than its damage-based rating indicates if its strongest winds occur away from suitable damage indicators, such as in an open field.[75][76] Outside Tornado Alley, and North America in general, violent tornadoes are extremely rare. This is apparently mostly due to the lesser number of tornadoes overall, as research shows that tornado intensity distributions are fairly similar worldwide. A few significant tornadoes occur annually in Europe, Asia, southern Africa, and southeastern South America.[77]
Climatology

The United States has the most tornadoes of any country, nearly four times more than estimated in all of Europe, excluding waterspouts.[78] This is mostly due to the unique geography of the continent. North America is a large continent that extends from the tropics north into arctic areas, and has no major east–west mountain range to block air flow between these two areas. In the middle latitudes, where most tornadoes of the world occur, the Rocky Mountains block moisture and buckle the atmospheric flow, forcing drier air at mid-levels of the troposphere due to downsloped winds, and causing the formation of a low pressure area downwind to the east of the mountains. Increased westerly flow off the Rockies force the formation of a dry line when the flow aloft is strong,[79] while the Gulf of Mexico fuels abundant low-level moisture in the southerly flow to its east. This unique topography allows for frequent collisions of warm and cold air, the conditions that breed strong, long-lived storms throughout the year. A large portion of these tornadoes form in an area of the central United States known as Tornado Alley.[80] This area extends into Canada, particularly Ontario and the Prairie Provinces, although southeast Quebec, the interior of British Columbia, and western New Brunswick are also tornado-prone.[81] Tornadoes also occur across northeastern Mexico.[5]
The United States averages about 1,200 tornadoes per year, followed by Canada, averaging 62 reported per year.[82] NOAA's has a higher average 100 per year in Canada.[83] The Netherlands has the highest average number of recorded tornadoes per area of any country (more than 20, or 0.00048/km2, 0.0012/sq mi annually), followed by the UK (around 33, 0.00013/km2, 0.00034/sq mi per year), although those are of lower intensity, briefer[84][85] and cause minor damage.[78]

Tornadoes kill an average of 179 people per year in Bangladesh, the most in the world.[86] Reasons for this include the region's high population density, poor construction quality, and lack of tornado safety knowledge.[86][87] Other areas of the world that have frequent tornadoes include South Africa, the La Plata Basin area, portions of Europe, Australia and New Zealand, and far eastern Asia.[8][88]
Tornadoes are most common in spring and least common in winter, but tornadoes can occur any time of year that favorable conditions occur.[26] Spring and fall experience peaks of activity as those are the seasons when stronger winds, wind shear, and atmospheric instability are present.[89] Tornadoes are focused in the right front quadrant of landfalling tropical cyclones, which tend to occur in the late summer and autumn. Tornadoes can also be spawned as a result of eyewall mesovortices, which persist until landfall.[90]
Tornado occurrence is highly dependent on the time of day, because of solar heating.[91] Worldwide, most tornadoes occur in the late afternoon, between 15:00 (3 pm) and 19:00 (7 pm) local time, with a peak near 17:00 (5 pm).[92][93][94][95][96] Destructive tornadoes can occur at any time of day. The Gainesville Tornado of 1936, one of the deadliest tornadoes in history, occurred at 8:30 am local time.[26]
The United Kingdom has the highest incidence of tornadoes per unit area of land in the world.[97] Unsettled conditions and weather fronts transverse the British Isles at all times of the years, and are responsible for spawning the tornadoes, which consequently form at all times of the year. The United Kingdom has at least 34 tornadoes per year and possibly as many as 50.[98] Most tornadoes in the United Kingdom are weak, but they are occasionally destructive. For example, the Birmingham tornado of 2005 and the London tornado of 2006 both registered F2 on the Fujita scale and both caused significant damage and injury.[99]
Associations with climate and climate change

Associations with various climate and environmental trends exist. For example, an increase in the sea surface temperature of a source region (e.g. Gulf of Mexico and Mediterranean Sea) increases atmospheric moisture content. Increased moisture can fuel an increase in severe weather and tornado activity, particularly in the cool season.[100]
Some evidence does suggest that the Southern Oscillation is weakly correlated with changes in tornado activity, which vary by season and region, as well as whether the ENSO phase is that of El Niño or La Niña.[101] Research has found that fewer tornadoes and hailstorms occur in winter and spring in the U.S. central and southern plains during El Niño, and more occur during La Niña, than in years when temperatures in the Pacific are relatively stable. Ocean conditions could be used to forecast extreme spring storm events several months in advance.[102]
Climatic shifts may affect tornadoes via teleconnections in shifting the jet stream and the larger weather patterns. The climate-tornado link is confounded by the forces affecting larger patterns and by the local, nuanced nature of tornadoes. Although it is reasonable to suspect that global warming may affect trends in tornado activity,[103] any such effect is not yet identifiable due to the complexity, local nature of the storms, and database quality issues. Any effect would vary by region.[104]
Detection

Rigorous attempts to warn of tornadoes began in the United States in the mid-20th century. Before the 1950s, the only method of detecting a tornado was by someone seeing it on the ground. Often, news of a tornado would reach a local weather office after the storm. However, with the advent of weather radar, areas near a local office could get advance warning of severe weather. The first public tornado warnings were issued in 1950 and the first tornado watches and convective outlooks came about in 1952. In 1953, it was confirmed that hook echoes were associated with tornadoes.[105] By recognizing these radar signatures, meteorologists could detect thunderstorms probably producing tornadoes from several miles away.[106]
Radar
Today most developed countries have a network of weather radars, which serves as the primary method of detecting hook signatures that are likely associated with tornadoes. In the United States and a few other countries, Doppler weather radar stations are used. These devices measure the velocity and radial direction (towards or away from the radar) of the winds within a storm, and so can spot evidence of rotation in storms from over 160 km (100 miles) away. When storms are distant from a radar, only areas high within the storm are observed and the important areas below are not sampled.[107] Data resolution also decreases with distance from the radar. Some meteorological situations leading to tornadogenesis are not readily detectable by radar and tornado development may occasionally take place more quickly than radar can complete a scan and send the batch of data. Doppler weather radar systems can detect mesocyclones within a supercell thunderstorm. This allows meteorologists to predict tornado formations throughout thunderstorms.[108]

Storm spotting
In the mid-1970s, the U.S. National Weather Service (NWS) increased its efforts to train storm spotters so they could spot key features of storms that indicate severe hail, damaging winds, and tornadoes, as well as storm damage and flash flooding. The program was called Skywarn, and the spotters were local sheriff's deputies, state troopers, firefighters, ambulance drivers, amateur radio operators, civil defense (now emergency management) spotters, storm chasers, and ordinary citizens. When severe weather is anticipated, local weather service offices request these spotters to look out for severe weather and report any tornadoes immediately, so that the office can warn of the hazard.[citation needed]
Spotters usually are trained by the NWS on behalf of their respective organizations, and report to them. The organizations activate public warning systems such as sirens and the Emergency Alert System (EAS), and they forward the report to the NWS.[109] There are more than 230,000 trained Skywarn weather spotters across the United States.[110]
In Canada, a similar network of volunteer weather watchers, called Canwarn, helps spot severe weather, with more than 1,000 volunteers.[111] In Europe, several nations are organizing spotter networks under the auspices of Skywarn Europe[112] and the Tornado and Storm Research Organisation (TORRO) has maintained a network of spotters in the United Kingdom since 1974.[113]
Storm spotters are required because radar systems such as NEXRAD detect signatures that suggest the presence of tornadoes, rather than tornadoes as such.[114] Radar may give a warning before there is any visual evidence of a tornado or an imminent one, but ground truth from an observer can give definitive information.[115] The spotter's ability to see what radar cannot is especially important as distance from the radar site increases, because the radar beam becomes progressively higher in altitude further away from the radar, chiefly due to curvature of Earth, and the beam also spreads out.[107]
Visual evidence

Storm spotters are trained to discern whether or not a storm seen from a distance is a supercell. They typically look to its rear, the main region of updraft and inflow. Under that updraft is a rain-free base, and the next step of tornadogenesis is the formation of a rotating wall cloud. The vast majority of intense tornadoes occur with a wall cloud on the backside of a supercell.[74]
Evidence of a supercell is based on the storm's shape and structure, and cloud tower features such as a hard and vigorous updraft tower, a persistent, large overshooting top, a hard anvil (especially when backsheared against strong upper level winds), and a corkscrew look or striations. Under the storm and closer to where most tornadoes are found, evidence of a supercell and the likelihood of a tornado includes inflow bands (particularly when curved) such as a "beaver tail", and other clues such as strength of inflow, warmth and moistness of inflow air, how outflow- or inflow-dominant a storm appears, and how far is the front flank precipitation core from the wall cloud. Tornadogenesis is most likely at the interface of the updraft and rear flank downdraft, and requires a balance between the outflow and inflow.[21]
Only wall clouds that rotate spawn tornadoes, and they usually precede the tornado between five and thirty minutes. Rotating wall clouds may be a visual manifestation of a low-level mesocyclone. Barring a low-level boundary, tornadogenesis is highly unlikely unless a rear flank downdraft occurs, which is usually visibly evidenced by evaporation of cloud adjacent to a corner of a wall cloud. A tornado often occurs as this happens or shortly afterwards; first, a funnel cloud dips and in nearly all cases by the time it reaches halfway down, a surface swirl has already developed, signifying a tornado is on the ground before condensation connects the surface circulation to the storm. Tornadoes may also develop without wall clouds, under flanking lines and on the leading edge. Spotters watch all areas of a storm, and the cloud base and surface.[116]
Extremes

The tornado which holds most records in history was the Tri-State Tornado, which roared through parts of Missouri, Illinois, and Indiana on March 18, 1925. It was likely an F5, though tornadoes were not ranked on any scale in that era. It holds records for longest path length (219 miles; 352 km), longest duration (about 3.5 hours), and fastest forward speed for a significant tornado (73 mph; 117 km/h) anywhere on Earth. In addition, it is the deadliest single tornado in United States history (695 dead).[26] The tornado was also the costliest tornado in history at the time (unadjusted for inflation), but in the years since has been surpassed by several others if population changes over time are not considered. When costs are normalized for wealth and inflation, it ranks third today.[117]
The deadliest tornado in world history was the Daultipur-Salturia Tornado in Bangladesh on April 26, 1989, which killed approximately 1,300 people.[86]Bangladesh has had at least 19 tornadoes in its history that killed more than 100 people, almost half of the total in the rest of the world.[citation needed]
One of the most extensive tornado outbreaks on record was the 1974 Super Outbreak, which affected a large area of the central United States and extreme southern Ontario on April 3 and 4, 1974. The outbreak featured 148 tornadoes in 18 hours, many of which were violent; seven were of F5 intensity, and twenty-three peaked at F4 strength. Sixteen tornadoes were on the ground at the same time during its peak. More than 300 people, possibly as many as 330, were killed.[118]
While direct measurement of the most violent tornado wind speeds is nearly impossible, since conventional anemometers would be destroyed by the intense winds and flying debris, some tornadoes have been scanned by mobile Doppler radar units, which can provide a good estimate of the tornado's winds. The highest wind speed ever measured in a tornado, which is also the highest wind speed ever recorded on the planet, is 301 ± 20 mph (484 ± 32 km/h) in the F5 Bridge Creek-Moore, Oklahoma, tornado which killed 36 people.[119] The reading was taken about 100 feet (30 m) above the ground.[3]
Storms that produce tornadoes can feature intense updrafts, sometimes exceeding 150 mph (240 km/h). Debris from a tornado can be lofted into the parent storm and carried a very long distance. A tornado which affected Great Bend, Kansas, in November 1915, was an extreme case, where a "rain of debris" occurred 80 miles (130 km) from the town, a sack of flour was found 110 miles (180 km) away, and a cancelled check from the Great Bend bank was found in a field outside of Palmyra, Nebraska, 305 miles (491 km) to the northeast.[120] Waterspouts and tornadoes have been advanced as an explanation for instances of raining fish and other animals.[121]
Safety

Though tornadoes can strike in an instant, there are precautions and preventative measures that can be taken to increase the chances of survival. Authorities such as the Storm Prediction Center in the United States advise having a pre-determined plan should a tornado warning be issued. When a warning is issued, going to a basement or an interior first-floor room of a sturdy building greatly increases chances of survival.[122] In tornado-prone areas, many buildings have underground storm cellars, which have saved thousands of lives.[123]
Some countries have meteorological agencies which distribute tornado forecasts and increase levels of alert of a possible tornado (such as tornado watches and warnings in the United States and Canada). Weather radios provide an alarm when a severe weather advisory is issued for the local area, mainly available only in the United States. Unless the tornado is far away and highly visible, meteorologists advise that drivers park their vehicles far to the side of the road (so as not to block emergency traffic), and find a sturdy shelter. If no sturdy shelter is nearby, getting low in a ditch is the next best option. Highway overpasses are one of the worst places to take shelter during tornadoes, as the constricted space can be subject to increased wind speed and funneling of debris underneath the overpass.[124]
Myths and misconceptions
Folklore often identifies a green sky with tornadoes, and though the phenomenon may be associated with severe weather, there is no evidence linking it specifically with tornadoes.[125] It is often thought that opening windows will lessen the damage caused by the tornado. While there is a large drop in atmospheric pressure inside a strong tornado, the pressure difference is unlikely to cause significant damage. Opening windows may instead increase the severity of the tornado's damage.[126] A violent tornado can destroy a house whether its windows are open or closed.[126][127] Another commonly held misconception is that highway overpasses provide adequate shelter from tornadoes. This belief is partly inspired by widely circulated video captured during the 1991 tornado outbreak near Andover, Kansas, where a news crew and several other people took shelter under an overpass on the Kansas Turnpike and safely rode out a tornado as it passed nearby.[128] However, a highway overpass is a dangerous place during a tornado, and the subjects of the video remained safe due to an unlikely combination of events: the storm in question was a weak tornado, the tornado did not directly strike the overpass,[128] and the overpass itself was of a unique design. Due to the Venturi effect, tornadic winds are accelerated in the confined space of an overpass.[129] Indeed, in the 1999 Oklahoma tornado outbreak of May 3, 1999, three highway overpasses were directly struck by tornadoes, and at each of the three locations there was a fatality, along with many life-threatening injuries.[130] By comparison, during the same tornado outbreak, more than 2,000 homes were completely destroyed and another 7,000 damaged, and yet only a few dozen people died in their homes.[124]
An old belief is that the southwest corner of a basement provides the most protection during a tornado. The safest place is the side or corner of an underground room opposite the tornado's direction of approach (usually the northeast corner), or the central-most room on the lowest floor. Taking shelter in a basement, under a staircase, or under a sturdy piece of furniture such as a workbench further increases the chances of survival.[126][127]
There are areas which people believe to be protected from tornadoes, whether by being in a city, near a major river, hill, or mountain, or even protected by supernatural forces.[131] Tornadoes have been known to cross major rivers, climb mountains,[132] affect valleys, and have damaged several city centers. As a general rule, no area is safe from tornadoes, though some areas are more susceptible than others.[28][126][127]
Ongoing research

Meteorology is a relatively young science and the study of tornadoes is newer still. Although researched for about 140 years and intensively so for around 60 years, there are still aspects of tornadoes which remain a mystery.[133] Meteorologists have a fairly good understanding of the development of thunderstorms and mesocyclones,[134][135] and the meteorological conditions conducive to their formation. However, the step from supercell, or other respective formative processes, to tornadogenesis and the prediction of tornadic vs. non-tornadic mesocyclones is not yet well known and is the focus of much research.[89]
Also under study are the low-level mesocyclone and the stretching of low-level vorticity which tightens into a tornado,[89] in particular, what are the processes and what is the relationship of the environment and the convective storm. Intense tornadoes have been observed forming simultaneously with a mesocyclone aloft (rather than succeeding mesocyclogenesis) and some intense tornadoes have occurred without a mid-level mesocyclone.[136]
In particular, the role of downdrafts, particularly the rear-flank downdraft, and the role of baroclinic boundaries, are intense areas of study.[137]
Reliably predicting tornado intensity and longevity remains a problem, as do details affecting characteristics of a tornado during its life cycle and tornadolysis. Other rich areas of research are tornadoes associated with mesovortices within linear thunderstorm structures and within tropical cyclones.[138]
Meteorologists still do not know the exact mechanisms by which most tornadoes form, and occasional tornadoes still strike without a tornado warning being issued.[139] Analysis of observations including both stationary and mobile (surface and aerial) in-situ and remote sensing (passive and active) instruments generates new ideas and refines existing notions. Numerical modeling also provides new insights as observations and new discoveries are integrated into our physical understanding and then tested in computer simulations which validate new notions as well as produce entirely new theoretical findings, many of which are otherwise unattainable. Importantly, development of new observation technologies and installation of finer spatial and temporal resolution observation networks have aided increased understanding and better predictions.[140]
Research programs, including field projects such as the VORTEX projects (Verification of the Origins of Rotation in Tornadoes Experiment), deployment of TOTO (the TOtable Tornado Observatory), Doppler on Wheels (DOW), and dozens of other programs, hope to solve many questions that still plague meteorologists.[49] Universities, government agencies such as the National Severe Storms Laboratory, private-sector meteorologists, and the National Center for Atmospheric Research are some of the organizations very active in research; with various sources of funding, both private and public, a chief entity being the National Science Foundation.[114][141] The pace of research is partly constrained by the number of observations that can be taken; gaps in information about the wind, pressure, and moisture content throughout the local atmosphere; and the computing power available for simulation.[142]
Solar storms similar to tornadoes have been recorded, but it is unknown how closely related they are to their terrestrial counterparts.[143]
Gallery
-
Rope Tornado near Yuma, Colorado on August 8, 2023.
-
A wall cloud with tornado South of Limon, Colorado.
-
Dash cam footage of the Lincoln, Nebraska EF3 tornado
-
A radar reflectivity image of a classic tornadic supercell near Oklahoma City, Oklahoma on May 3, 1999.
-
Classic hook echo can be seen for this Kansas EF2 tornado in 2024
-
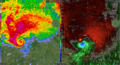
A Doppler on Wheels image of a tornadic thunderstorm near La Grange, Wyoming (USA) captured during the VORTEX2 project. In the velocity image on the left, Blues/green represent winds moving towards the radar, and reds/yellows indicate winds moving away from the radar. In the reflectivity image on the right, the main body of the storm can be seen, with the appendage on the bottom of the storm being a hook echo.
See also
- Cultural significance of tornadoes
- Cyclone
- Derecho
- List of tornadoes and tornado outbreaks
- List of tropical cyclone-spawned tornadoes
- List of tornadoes with confirmed satellite tornadoes
- Secondary flow
- Skipping tornado
- Space tornado
- Tornado preparedness
- Tornadoes of 2024
- Tropical cyclone
- Hypercane
- Typhoon
- Vortex
- Whirlwind
References
- ^ "merriam-webster.com". merriam-webster.com. Archived from the original on 2017-07-09. Retrieved 2012-09-03.
- ^ Garrison, Tom (2012). Essentials of Oceanography. Cengage Learning. ISBN 978-0-8400-6155-3.
- ^ a b Wurman, Joshua (2008-08-29). "Doppler on Wheels". Center for Severe Weather Research. Archived from the original on 2007-02-05. Retrieved 2009-12-13.
- ^ a b "Hallam Nebraska Tornado". National Weather Service. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. 2005-10-02. Archived from the original on 2013-04-30. Retrieved 2009-11-15.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Edwards, Roger (2006-04-04). "The Online Tornado FAQ". Storm Prediction Center. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original on 2006-09-29. Retrieved 2006-09-08.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ National Weather Service (2009-02-03). "15 January 2009: Lake Champlain Sea Smoke, Steam Devils, and Waterspout: Chapters IV and V". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original on 2016-01-01. Retrieved 2009-06-21.
- ^ "Tornado Alley, USA: Science News Online, May 11, 2002". 25 August 2006. Archived from the original on 25 August 2006.
- ^ a b "Tornado: Global occurrence". Encyclopædia Britannica Online. 2009. Archived from the original on 2007-03-17. Retrieved 2009-12-13.
- ^ "TORNADO CENTRAL, Where Tornadoes Strike Around the World, February 12, 2018". 12 February 2018. Archived from the original on 30 September 2021. Retrieved 30 September 2021.
- ^ Coleman, Timothy A.; Knupp, Kevin R.; Spann, James; Elliott, J. B.; Peters, Brian E. (2011-05-01). "The History (and Future) of Tornado Warning Dissemination in the United States". Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society. 92 (5): 567–582. Bibcode:2011BAMS...92..567C. doi:10.1175/2010BAMS3062.1.
- ^ Ahrens, C. Donald (2016). Meteorology today: an introduction to weather, climate, and the environment (11th ed.). Boston, MA, USA: Cengage Learning. ISBN 978-1-305-11358-9.
- ^ Meaden, Terrance (2004). "Wind Scales: Beaufort, T – Scale, and Fujita's Scale". Tornado and Storm Research Organisation. Archived from the original on 2010-04-30. Retrieved 2009-09-11.
- ^ "The International Fujita (IF) Scale Tornado and Wind Damage Assessment Guide" (PDF). ESSL.org. European Severe Storms Laboratory. Archived (PDF) from the original on 28 April 2022. Retrieved 26 June 2022.
- ^ "Enhanced F Scale for Tornado Damage". Storm Prediction Center. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. 2007-02-01. Archived from the original on 2012-07-11. Retrieved 2009-06-21.
- ^ Edwards, Roger; Ladue, James G.; Ferree, John T.; Scharfenberg, Kevin; Maier, Chris; Coulbourne, William L. (2013). "Tornado Intensity Estimation: Past, Present, and Future". Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society. 94 (5): 641–653. Bibcode:2013BAMS...94..641E. doi:10.1175/BAMS-D-11-00006.1. S2CID 7842905.
- ^ a b Harper, Douglas. "tornado". Online Etymology Dictionary. Retrieved 2009-12-13.
- ^ Mish, Frederick C. (1993). Merriam Webster's Collegiate Dictionary (10 ed.). Merriam-Webster, Incorporated. ISBN 0-87779-709-9. Retrieved 2009-12-13.
- ^ a b Marshall, Tim (2008-11-09). "The Tornado Project's Terrific, Timeless and Sometimes Trivial Truths about Those Terrifying Twirling Twisters!". The Tornado Project. Archived from the original on 2008-10-16. Retrieved 2008-11-09.
- ^ "Frequently Asked Questions about Tornadoes". National Severe Storms Laboratory. 2009-07-20. Archived from the original on 2012-05-23. Retrieved 2010-06-22.
- ^ a b Glossary of Meteorology (2020). Tornado (2 ed.). American Meteorological Society. Archived from the original on 2021-05-08. Retrieved 2021-03-06.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Advanced Spotters' Field Guide" (PDF). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. 2003-01-03. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-10-09. Retrieved 2009-12-13.
- ^ Doswell, Charles A. III (2001-10-01). "What is a tornado?". Cooperative Institute for Mesoscale Meteorological Studies. Archived from the original on 2018-07-03. Retrieved 2008-05-28.
- ^ Renno, Nilton O. (2008-07-03). "A thermodynamically general theory for convective vortices" (PDF). Tellus A. 60 (4): 688–99. Bibcode:2008TellA..60..688R. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0870.2008.00331.x. hdl:2027.42/73164. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-10-09. Retrieved 2009-12-12.
- ^ Funnel cloud (2 ed.). American Meteorological Society. 2000-06-30. Archived from the original on 2013-02-05. Retrieved 2009-02-25.
- ^ Branick, Michael (2006). "A Comprehensive Glossary of Weather Terms for Storm Spotters". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original on 2003-08-03. Retrieved 2007-02-27.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Grazulis, Thomas P. (July 1993). Significant Tornadoes 1680–1991. St. Johnsbury, VT: The Tornado Project of Environmental Films. ISBN 1-879362-03-1.
- ^ Schneider, Russell S.; Brooks, Harold E. & Schaefer, Joseph T. (2004). "Tornado Outbreak Day Sequences: Historic Events and Climatology (1875–2003)" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-10-09. Retrieved 2007-03-20.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Lyons, Walter A. (1997). "Tornadoes". The Handy Weather Answer Book (2nd ed.). Detroit, Michigan: Visible Ink press. pp. 175–200. ISBN 0-7876-1034-8.
- ^ a b Edwards, Roger (2008-07-18). "Wedge Tornado". National Weather Service. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original on 2021-05-11. Retrieved 2007-02-28.
- ^ a b Singer, Oscar (May–July 1985). "27.0.0 General Laws Influencing the Creation of Bands of Strong Bands". Bible of Weather Forecasting. 1 (4): 57–58.
- ^ Edwards, Roger (2008-07-18). "Rope Tornado". National Weather Service. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original on 2007-07-11. Retrieved 2007-02-28.
- ^ "May 31–June 1, 2013 Tornado and Flash Flood Event: The May 31, 2013 El Reno, OK Tornado". National Weather Service Weather Forecast Office. Norman, Oklahoma: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. July 28, 2014. Archived from the original on July 25, 2015. Retrieved December 25, 2014.
- ^ Doswell, Charles A. III. "The Tri-State Tornado of 18 March 1925". Reanalysis Project. Archived from the original (Powerpoint Presentation) on 2007-06-14. Retrieved 2007-04-07.
- ^ a b Edwards, Roger (2009). "Public Domain Tornado Images". National Weather Service. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original on 2006-09-30. Retrieved 2009-11-17.
- ^ a b Linda Mercer Lloyd (1996). Target: Tornado (Videotape). The Weather Channel.
- ^ "The Basics of Storm Spotting". National Weather Service. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. 2009-01-15. Archived from the original on 2003-10-11. Retrieved 2009-11-17.
- ^ Peterson, Franklynn; Kwsselman, Judi R (July 1978). "Tornado factory – giant simulator probes killer twisters". Popular Science. 213 (1): 76–78.
- ^ Monastersky, R. (1999-05-15). "Oklahoma Tornado Sets Wind Record". Science News. pp. 308–09. Archived from the original on 2015-04-02. Retrieved 2006-10-20.
- ^ Justice, Alonzo A. (1930). "Seeing the Inside of a Tornado". Monthly Weather Review. 58 (5): 205–06. Bibcode:1930MWRv...58..205J. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1930)58<205:STIOAT>2.0.CO;2.
- ^ Hall, Roy S. (2003). "Inside a Texas Tornado". Tornadoes. Greenhaven Press. pp. 59–65. ISBN 0-7377-1473-5.
- ^ Davies-Jones, Robert (1984). "Streamwise Vorticity: The Origin of Updraft Rotation in Supercell Storms". J. Atmos. Sci. 41 (20): 2991–3006. Bibcode:1984JAtS...41.2991D. doi:10.1175/1520-0469(1984)041<2991:SVTOOU>2.0.CO;2.
- ^ Rotunno, Richard; Klemp, Joseph (1985). "On the Rotation and Propagation of Simulated Supercell Thunderstorms". J. Atmos. Sci. 42 (3): 271–92. Bibcode:1985JAtS...42..271R. doi:10.1175/1520-0469(1985)042<0271:OTRAPO>2.0.CO;2. Archived from the original on 2019-08-01. Retrieved 2019-08-01.
- ^ Wicker, Louis J.; Wilhelmson, Robert B. (1995). "Simulation and Analysis of Tornado Development and Decay within a Three-Dimensional Supercell Thunderstorm". J. Atmos. Sci. 52 (15): 2675–703. Bibcode:1995JAtS...52.2675W. doi:10.1175/1520-0469(1995)052<2675:SAAOTD>2.0.CO;2.
- ^ Forbes, Greg (2006-04-26). "anticyclonic tornado in El Reno, OK". The Weather Channel. Archived from the original on 2007-10-11. Retrieved 2006-12-30.
- ^ Monteverdi, John (2003-01-25). "Sunnyvale and Los Altos, CA Tornadoes 1998-05-04". Archived from the original on 2013-06-13. Retrieved 2006-10-20.
- ^ Abdullah, Abdul (April 1966). "The "Musical" Sound Emitted by a Tornado"" (PDF). Mon. Wea. Rev. 94 (4): 213–20. Bibcode:1966MWRv...94..213A. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.395.3099. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1966)094<0213:TMSEBA>2.3.CO;2. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2017-09-21.
- ^ Hoadley, David K. (1983-03-31). "Tornado Sound Experiences". Storm Track. 6 (3): 5–9. Archived from the original on 2012-06-19.
- ^ Bedard, A. J. (January 2005). "Low-Frequency Atmospheric Acoustic Energy Associated with Vortices Produced by Thunderstorms". Mon. Wea. Rev. 133 (1): 241–63. Bibcode:2005MWRv..133..241B. doi:10.1175/MWR-2851.1. S2CID 1004978.
- ^ a b c Bluestein, Howard (1999). "A History of Severe-Storm-Intercept Field Programs". Weather Forecast. 14 (4): 558–77. Bibcode:1999WtFor..14..558B. doi:10.1175/1520-0434(1999)014<0558:AHOSSI>2.0.CO;2.
- ^ Tatom, Frank; Knupp, Kevin R. & Vitto, Stanley J. (1995). "Tornado Detection Based on Seismic Signal". J. Appl. Meteorol. 34 (2): 572–82. Bibcode:1995JApMe..34..572T. doi:10.1175/1520-0450(1995)034<0572:TDBOSS>2.0.CO;2.
- ^ Leeman, John R.; Schmitter, E. D. (April 2009). "Electric signals generated by tornados". Atmos. Res. 92 (2): 277–79. Bibcode:2009AtmRe..92..277L. doi:10.1016/j.atmosres.2008.10.029.
- ^ Samaras, Timothy M. (October 2004). "A Historical Perspective of In-Situ Observations within Tornado Cores". Preprints of the 22nd Conf. Severe Local Storms. Hyannis, MA: American Meteorological Society. Archived from the original on 2011-01-15. Retrieved 2007-05-23.
- ^ Perez, Antony H.; Wicker, Louis J. & Orville, Richard E. (1997). "Characteristics of Cloud-to-Ground Lightning Associated with Violent Tornadoes". Weather Forecast. 12 (3): 428–37. Bibcode:1997WtFor..12..428P. doi:10.1175/1520-0434(1997)012<0428:COCTGL>2.0.CO;2.
- ^ Lee, Julian J.; Samaras, Timothy P.; Young, Carl R. (2004-10-07). "Pressure Measurements at the ground in an F-4 tornado". Preprints of the 22nd Conf. Severe Local Storms. Hyannis, Massachusetts: American Meteorological Society. Archived from the original on 2011-06-09. Retrieved 2007-07-06.
- ^ "Radar Signatures for Severe Convective Weather: Low-Level Mesocyclone, Print Version". www.faculty.luther.edu. Retrieved 2022-06-03.
- ^ US Department of Commerce, NOAA. "Supercell Structure and Dynamics". www.weather.gov. Archived from the original on 2022-05-26. Retrieved 2022-06-03.
- ^ Howard, Brian Clark (May 11, 2015). "How Tornadoes Form and Why They're so Unpredictable". National Geographic News. National Geographic. Archived from the original on May 14, 2015. Retrieved 2015-05-11.
- ^ "Tornado Types". NOAA National Severe Storms Laboratory. Archived from the original on 2023-03-27. Retrieved 2023-03-28.
- ^ "The Online Tornado FAQ". www.spa.noaa.gov. Roger Edwards, Storm Prediction Center. March 2016. Archived from the original on 2 March 2012. Retrieved 27 October 2016.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Ben-Amots, N. (2016). "Dynamics and thermodynamics of tornado: Rotation effects". Atmospheric Research. 178–179: 320–328. Bibcode:2016AtmRe.178..320B. doi:10.1016/j.atmosres.2016.03.025.
- ^ Tao, Tianyou; Wang, Hao; Yao, Chengyuan; Zou, Zhongqin; Xu, Zidog (2018). "Performance of structures and infrastructures facilities during an EF4 tornado in Yancheng". Wind and Structure. 27 (2): 137–147. doi:10.12989/was.2018.27.2.137.
- ^ Markowski, Paul M.; Straka, Jerry M.; Rasmussen, Erik N. (2003). "Tornadogenesis Resulting from the Transport of Circulation by a Downdraft: Idealized Numerical Simulations". J. Atmos. Sci. 60 (6): 795–823. Bibcode:2003JAtS...60..795M. doi:10.1175/1520-0469(2003)060<0795:TRFTTO>2.0.CO;2.
- ^ Zittel, Dave (2000-05-04). "Tornado Chase 2000". USA Today. Archived from the original on 2007-01-04. Retrieved 2007-05-19.
- ^ Golden, Joseph (2007-11-01). "Waterspouts are tornadoes over water". USA Today. Archived from the original on 2012-09-07. Retrieved 2007-05-19.
- ^ Grazulis, Thomas P.; Flores, Dan (2003). The Tornado: Nature's Ultimate Windstorm. Norman OK: University of Oklahoma Press. p. 256. ISBN 0-8061-3538-7.
- ^ "About Waterspouts". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. 2007-01-04. Archived from the original on 2009-09-13. Retrieved 2009-12-13.
- ^ "European Severe Weather Database definitions". 2012-01-02. Archived from the original on 2012-07-08. Retrieved 2012-06-11.
- ^ "Gustnado". Glossary of Meteorology. American Meteorological Society. June 2000. Archived from the original on 2007-09-30. Retrieved 2006-09-20.
- ^ Jones, Charles H.; Liles, Charlie A. (1999). "Severe Weather Climatology for New Mexico". Archived from the original on 2018-10-21. Retrieved 2006-09-29.
- ^ "The Fujita Scale of Tornado Intensity". Archived from the original on 2011-12-30. Retrieved 2013-05-08.
- ^ "Goshen County Tornado Given Official Rating of EF2". National Weather Service. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original on 2010-05-28. Retrieved 2009-11-21.
- ^ Lewellen, David C.; Zimmerman, M. I. (2008-10-28). Using Simulated Tornado Surface Marks to Decipher Near-Ground Winds (PDF). 24th Conf. Severe Local Storms. American Meteorological Society. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-10-09. Retrieved 2009-12-09.
- ^ Brooks, Harold E. (2004-04-01). "On the Relationship of Tornado Path Length and Width to Intensity". Weather and Forecasting. 19 (2): 310–319. Bibcode:2004WtFor..19..310B. doi:10.1175/1520-0434(2004)019<0310:OTROTP>2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0882-8156.
- ^ a b "basic Spotters' Field Guide" (PDF). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, National Weather Service. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-10-09.
- ^ Bluestein, Howard B.; Snyder, Jeffrey C.; Houser, Jana B. (2015). "A Multiscale Overview of the el Reno, Oklahoma, Tornadic Supercell of 31 May 2013". Weather and Forecasting. 30 (3): 525–552. Bibcode:2015WtFor..30..525B. doi:10.1175/WAF-D-14-00152.1.
- ^ Wurman, Joshua; Kosiba, Karen; White, Trevor; Robinson, Paul (6 April 2021). "Supercell tornadoes are much stronger and wider than damage-based ratings indicate". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 118 (14): e2021535118. Bibcode:2021PNAS..11821535W. doi:10.1073/pnas.2021535118. PMC 8040662. PMID 33753558.
- ^ Dotzek, Nikolai; Grieser, Jürgen; Brooks, Harold E. (2003-03-01). "Statistical modeling of tornado intensity distributions". Atmos. Res. 67: 163–87. Bibcode:2003AtmRe..67..163D. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.490.4573. doi:10.1016/S0169-8095(03)00050-4.
- ^ a b Dotzek, Nikolai (2003-03-20). "An updated estimate of tornado occurrence in Europe". Atmos. Res. 67–68: 153–161. Bibcode:2003AtmRe..67..153D. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.669.2418. doi:10.1016/S0169-8095(03)00049-8.
- ^ Huaqing Cai (2001-09-24). "Dryline cross section". University of California Los Angeles. Archived from the original on 2008-01-20. Retrieved 2009-12-13.
- ^ Perkins, Sid (2002-05-11). "Tornado Alley, USA". Science News. pp. 296–98. Archived from the original on 2006-08-25. Retrieved 2006-09-20.
- ^ "Tornadoes". Prairie Storm Prediction Centre. Environment Canada. 2007-10-07. Archived from the original on 2001-03-09. Retrieved 2009-12-13.
- ^ Vettese, Dayna. "Tornadoes in Canada: Everything you need to know". The Weather Network. Archived from the original on 27 November 2016. Retrieved 26 November 2016.
- ^ "U.S. Tornado Climatology". NOAA. Archived from the original on 9 December 2016. Retrieved 26 November 2016.
- ^ Holden, J.; Wright, A. (2003-03-13). "UK tornado climatology and the development of simple prediction tools" (PDF). Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 130 (598): 1009–21. Bibcode:2004QJRMS.130.1009H. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.147.4293. doi:10.1256/qj.03.45. S2CID 18365306. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-08-24. Retrieved 2009-12-13.
- ^ "Natural Disasters: Tornadoes". BBC Science and Nature. BBC. 2002-03-28. Archived from the original on 2002-10-14. Retrieved 2009-12-13.
- ^ a b c Bimal Kanti Paul; Rejuan Hossain Bhuiyan (2005-01-18). "The April 2004 Tornado in North-Central Bangladesh: A Case for Introducing Tornado Forecasting and Warning Systems" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2010-06-06. Retrieved 2009-12-13.
- ^ Finch, Jonathan (2008-04-02). "Bangladesh and East India Tornadoes Background Information". Archived from the original on 2009-09-01. Retrieved 2009-12-13.
- ^ Graf, Michael (2008-06-28). "Synoptical and mesoscale weather situations associated with tornadoes in Europe" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-03. Retrieved 2009-12-13.
- ^ a b c "Structure and Dynamics of Supercell Thunderstorms". National Weather Service. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. 2008-08-28. Archived from the original on 2009-11-17. Retrieved 2009-12-13.
- ^ "Frequently Asked Questions: Are TC tornadoes weaker than midlatitude tornadoes?". Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory, Hurricane Research Division. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. 2006-10-04. Archived from the original on 2009-09-14. Retrieved 2009-12-13.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Kelly; et al. (1978). "An Augmented Tornado Climatology". Mon. Wea. Rev. 106 (8): 1172–1183. Bibcode:1978MWRv..106.1172K. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1978)106<1172:AATC>2.0.CO;2.
- ^ "Tornado: Diurnal patterns". Encyclopædia Britannica Online. 2007. p. G.6. Archived from the original on 2008-05-02. Retrieved 2009-12-13.
- ^ Holzer, A. M. (2000). "Tornado Climatology of Austria". Atmos. Res. 56 (1–4): 203–11. Bibcode:2001AtmRe..56..203H. doi:10.1016/S0169-8095(00)00073-9. Archived from the original on 2007-02-19. Retrieved 2007-02-27.
- ^ Dotzek, Nikolai (2000-05-16). "Tornadoes in Germany". Atmos. Res. 56 (1): 233–51. Bibcode:2001AtmRe..56..233D. doi:10.1016/S0169-8095(00)00075-2.
- ^ "South African Tornadoes". South African Weather Service. 2003. Archived from the original on 2007-05-26. Retrieved 2009-12-13.
- ^ Finch, Jonathan D.; Dewan, Ashraf M. (2007-05-23). "Bangladesh Tornado Climatology". Archived from the original on 2011-07-25. Retrieved 2009-12-13.
- ^ "TORRO | Research ~ Tornadoes ~ Background". www.torro.org.uk. Archived from the original on 2022-01-20. Retrieved 2022-01-20.
- ^ "Tornado FAQ's". www.torro.org.uk. Archived from the original on 2017-03-13. Retrieved 2017-03-12.
- ^ Coughlan, Sean (15 June 2015). "UK's 'tornado alley' identified". BBC News. Archived from the original on 22 December 2018. Retrieved 22 June 2018.
- ^ Edwards, Roger; Weiss, Steven J. (1996-02-23). "Comparisons between Gulf of Mexico Sea Surface Temperature Anomalies and Southern U.S. Severe Thunderstorm Frequency in the Cool Season". 18th Conf. Severe Local Storms. American Meteorological Society. Archived from the original on 2008-05-03. Retrieved 2008-01-07.
- ^ Cook, Ashton Robinson; Schaefer, Joseph T. (2008-01-22). "The Relation of El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO) to Winter Tornado Outbreaks". 19th Conf. Probability and Statistics. American Meteorological Society. Archived from the original on 2008-12-06. Retrieved 2009-12-13.
- ^ "El Niño brings fewer tornados". Nature. 519. 26 March 2015. Archived from the original on 19 July 2016. Retrieved 27 March 2016.
- ^ Trapp, Robert J.; Diffenbaugh, NS; Brooks, H. E.; Baldwin, M. E.; Robinson, E. D. & Pal, J. S. (2007-12-12). "Changes in severe thunderstorm environment frequency during the 21st century caused by anthropogenically enhanced global radiative forcing". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 104 (50): 19719–23. Bibcode:2007PNAS..10419719T. doi:10.1073/pnas.0705494104. PMC 2148364.
- ^ Solomon, Susan; et al. (2007). Climate Change 2007 – The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge, UK and New York: Cambridge University Press for the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. ISBN 978-0-521-88009-1. Archived from the original on 2007-05-01. Retrieved 2009-12-13.
- ^ "The First Tornadic Hook Echo Weather Radar Observations". Colorado State University. 2008. Archived from the original on 2008-08-20. Retrieved 2008-01-30.
- ^ Markowski, Paul M. (April 2002). "Hook Echoes and Rear-Flank Downdrafts: A Review". Mon. Wea. Rev. 130 (4): 852–76. Bibcode:2002MWRv..130..852M. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(2002)130<0852:HEARFD>2.0.CO;2. S2CID 54785955.
- ^ a b Airbus (2007-03-14). "Flight Briefing Notes: Adverse Weather Operations Optimum Use of Weather Radar" (PDF). SKYbrary. p. 2. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-10-09. Retrieved 2009-11-19.
- ^ "Research tools: Radar". www.nssl.noaa.gov. NOAA National Severe Storms Laboratory. Archived from the original on 2016-10-14. Retrieved October 14, 2016.
- ^ Doswell, Charles A. III; Moller, Alan R.; Brooks, Harold E. (1999). "Storm Spotting and Public Awareness since the First Tornado Forecasts of 1948" (PDF). Weather Forecast. 14 (4): 544–57. Bibcode:1999WtFor..14..544D. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.583.5732. doi:10.1175/1520-0434(1999)014<0544:SSAPAS>2.0.CO;2. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-10-09.
- ^ National Weather Service (2009-02-06). "What is SKYWARN?". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original on 2009-12-10. Retrieved 2009-12-13.
- ^ "Tornado Detection at Environment Canada". Environment Canada. 2004-06-02. Archived from the original on 2010-04-07. Retrieved 2009-12-13.
- ^ European Union (2009-05-31). "Skywarn Europe". Archived from the original on 2009-09-17. Retrieved 2009-12-13.
- ^ Meaden, Terence (1985). "A Brief History". Tornado and Storm Research Organisation. Archived from the original on 2015-06-26. Retrieved 2009-12-13.
- ^ a b National Severe Storms Laboratory (2006-11-15). "Detecting Tornadoes: What Does a Tornado Look Like?". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original on 2012-05-23. Retrieved 2009-12-13.
- ^ Edwards, Roger; Edwards, Elke (2003). "Proposals For Changes in Severe Local Storm Warnings, Warning Criteria and Verification". Archived from the original on 2009-06-28. Retrieved 2009-12-13.
- ^ "Questions and Answers about Tornadoes". A Severe Weather Primer. National Severe Storms Laboratory. 2006-11-15. Archived from the original on 2012-08-09. Retrieved 2007-07-05.
- ^ Brooks, Harold E.; Doswell, Charles A. III (2000-10-01). "Normalized Damage from Major Tornadoes in the United States: 1890–1999". Weather Forecast. 16 (1): 168–176. Bibcode:2001WtFor..16..168B. doi:10.1175/1520-0434(2001)016<0168:ndfmti>2.0.co;2. Archived from the original on 2007-02-08. Retrieved 2007-02-28.
- ^ Hoxit, Lee R.; Chappell, Charles F. (1975-11-01). "Tornado Outbreak of April 3–4, 1974; Synoptic Analysis" (PDF). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original on 2020-09-30. Retrieved 2009-12-13.
- ^ Anatomy of May 3's F5 tornado Archived 2010-05-23 at the Wayback Machine, The Oklahoman Newspaper, May 1, 2009
- ^ Grazulis, Thomas P. (2005-09-20). "Tornado Oddities". Archived from the original on 2009-05-07. Retrieved 2009-12-13.
- ^ Yahr, Emily (2006-02-21). "Q: You've probably heard the expression, "it's raining cats and dogs." Has it ever rained animals?". USA Today. Archived from the original on 2010-05-24. Retrieved 2009-12-13.
- ^ Edwards, Roger (2008-07-16). "Tornado Safety". National Weather Service. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original on 2009-08-25. Retrieved 2009-11-17.
- ^ "Storm Shelters" (PDF). National Weather Service. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. 2002-08-26. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2006-02-23. Retrieved 2009-12-13.
- ^ a b "Highway Overpasses as Tornado Shelters". National Weather Service. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. 2000-03-01. Archived from the original on 2000-06-16. Retrieved 2007-02-28.
- ^ Knight, Meredith (2011-04-18). "Fact or Fiction?: If the Sky Is Green, Run for Cover – A Tornado Is Coming". Scientific American. Archived from the original on 2012-10-14. Retrieved 2012-09-03.
- ^ a b c d Marshall, Tim (2005-03-15). "Myths and Misconceptions about Tornadoes". The Tornado Project. Archived from the original on 2013-06-08. Retrieved 2007-02-28.
- ^ a b c Grazulis, Thomas P. (2001). "Tornado Myths". The Tornado: Nature's Ultimate Windstorm. University of Oklahoma Press. ISBN 0-8061-3258-2.
- ^ a b National Weather Service Forecast Office. "Overpasses and Tornado Safety: Not a Good Mix". Tornado Overpass Information. Dodge City, Kansas: NOAA. Archived from the original on 7 January 2012. Retrieved 24 March 2012.
- ^ Climate Services and Monitoring Division (2006-08-17). "Tornado Myths, Facts, and Safety". National Climatic Data Center. Archived from the original on 2012-03-14. Retrieved 2012-03-27.
- ^ Cappella, Chris (2005-05-17). "Overpasses are tornado death traps". USA Today. Archived from the original on 2005-04-08. Retrieved 2007-02-28.
- ^ Dewey, Kenneth F. (2002-07-11). "Tornado Myths & Tornado Reality". High Plains Regional Climate Center and University of Nebraska–Lincoln. Archived from the original on June 11, 2008. Retrieved 2009-11-17.
- ^ Monteverdi, John; Edwards, Roger; Stumpf, Greg; Gudgel, Daniel (2006-09-13). "Tornado, Rockwell Pass, Sequoia National Park, 2004-07-07". Archived from the original on 2015-08-19. Retrieved 2009-11-19.
- ^ National Severe Storms Laboratory (2006-10-30). "VORTEX: Unraveling the Secrets". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original on 2012-11-03. Retrieved 2007-02-28.
- ^ Mogil, Michael H. (2007). Extreme Weather. New York: Black Dog & Leventhal Publisher. pp. 210–11. ISBN 978-1-57912-743-5.
- ^ McGrath, Kevin (1998-11-05). "Mesocyclone Climatology Project". University of Oklahoma. Archived from the original on 2010-07-09. Retrieved 2009-11-19.
- ^ Seymour, Simon (2001). Tornadoes. New York City: HarperCollins. p. 32. ISBN 0-06-443791-4.
- ^ Grazulis, Thomas P. (2001). The tornado: nature's ultimate windstorm. University of Oklahoma Press. pp. 63–65. ISBN 0-8061-3258-2. Retrieved 2009-11-20.
intense tornadoes without a mesocyclone.
- ^ Rasmussen, Erik (2000-12-31). "Severe Storms Research: Tornado Forecasting". Cooperative Institute for Mesoscale Meteorological Studies. Archived from the original on April 7, 2007. Retrieved 2007-03-27.
- ^ United States Environmental Protection Agency (2009-09-30). "Tornadoes". Archived from the original on 2012-05-12. Retrieved 2009-11-20.
- ^ Grazulis, Thomas P. (2001). The tornado: nature's ultimate windstorm. University of Oklahoma Press. pp. 65–69. ISBN 978-0-8061-3258-7. Retrieved 2009-11-20.
intense tornadoes without a mesocyclone.
- ^ National Center for Atmospheric Research (2008). "Tornadoes". University Corporation for Atmospheric Research. Archived from the original on 2010-04-23. Retrieved 2009-11-20.
- ^ "Scientists Chase Tornadoes to Solve Mysteries". NPR.org. 2010-04-09. Archived from the original on 2014-04-26. Retrieved 2014-04-26.
- ^ "Huge tornadoes discovered on the Sun". Physorg.com. Archived from the original on 2024-06-04. Retrieved 2012-09-03.
Further reading
- Bluestein, Howard B. (1999). Tornado Alley: Monster Storms of the Great Plains. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-510552-4.
- Bradford, Marlene (2001). Scanning the Skies: A History of Tornado Forecasting. Norman, OK: University of Oklahoma Press. ISBN 0-8061-3302-3.
- Grazulis, Thomas P. (January 1997). Significant Tornadoes Update, 1992–1995. St. Johnsbury, VT: Environmental Films. ISBN 1-879362-04-X.
- Pybus, Nani (Spring 2016). "'Cyclone' Jones: Dr. Herbert L. Jones and the Origins of Tornado Research in Oklahoma". Chronicles of Oklahoma. 94: 4–31. Retrieved May 5, 2022. Heavily illustrated.
External links
- NOAA Storm Events Database 1950–present
- European Severe Weather Database
- Tornado Detection and Warnings
- Electronic Journal of Severe Storms Meteorology
- NOAA Tornado Preparedness Guide
- Tornado History Project – Maps and statistics from 1950 to present
- "What we know and don’t know about tornado formation", Physics Today, September 2014
- U.S. Billion-dollar Weather and Climate Disasters